Dog owners know their pets hold a special place in their hearts and homes. Every wag and bark tells a story. It’s easy to forget the hidden complexities behind these creatures we cherish.
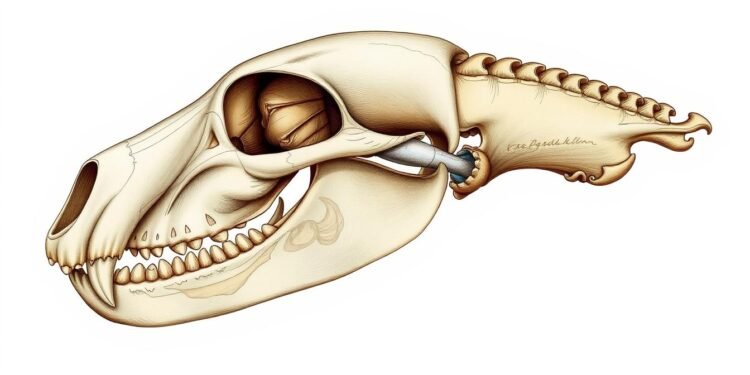
Have you ever thought about what lies beneath that furry exterior? The dog skull is more than just bones. It shows evolution, breed variation, and functionality that shapes our canine companions. Understanding dog skull anatomy helps us appreciate how different breeds have adapted over time.
In this guide, we’ll explore the dog skull’s anatomy and how it varies across breeds. We’ll look at the essential features that help dogs sense their world and eat. With insights from a study of 50 dogs, we aim to deepen your appreciation of the dog skull and its importance in the world of canines.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Dog Skull Anatomy
The dog skull is key to understanding how dogs see and eat. It’s made of about 50 bones, many in pairs. This shows how dogs evolved over time, influenced by humans and nature.
Dogs have been with humans for over 135,000 years. They changed a lot, including their skulls. Their brains got bigger compared to their bodies, but are still smaller than wolves’.
Today, there are about 400 dog breeds, each with its own skull shape. These shapes are divided into three main types:
- Dolichocephalic: Long, narrow heads like collies and wolfhounds.
- Mesocephalic: Medium-sized heads, found in German shepherds and beagles.
- Brachycephalic: Short, wide heads, seen in Boston terriers and Pekingese.
Dogs’ varied skull shapes come from selective breeding. This has led to interesting traits, like the bulldog’s short nose. Research shows that these traits are complex, influenced by many genes.
Studying the dog skull helps us understand how they eat and sense their world. It’s important for anyone interested in dogs, veterinary science, or the amazing variety of dog breeds.
Understanding Canine Skull Shapes
Dogs come in many shapes and sizes, each with its own skull type. These types are brachycephalic, mesocephalic, and dolichocephalic. Each type has its own look and health effects.
Brachycephalic Dogs
Brachycephalic dogs, like pugs and bulldogs, have short, wide skulls. This can cause dental problems, like underbites. They have the same number of teeth as other dogs but their mouths are too short, leading to gum disease.
Their skull shape also makes breathing hard. This can lead to serious breathing problems.
Mesocephalic Dogs
Mesocephalic dogs, like Labradors and German Shepherds, have medium-length skulls. They usually don’t have as many dental problems as brachycephalic dogs. Their skulls are big enough for their teeth, which helps prevent gum disease.
This shape also fits well with their eating habits. It’s based on their natural hunting instincts.
Dolichocephalic Dogs
Dolichocephalic dogs, like Greyhounds and Borzois, have long, narrow skulls. They might not have as many dental issues as brachycephalic dogs. But, they can get sick in their noses more easily.
This is because their noses are long and narrow. It can cause health problems as they get older.
Key Features of Dog Skull Anatomy
Understanding dog skull anatomy means looking at the details of its bones. These bones show the special canine skull features that different breeds have. A dog’s skull is made up of many bones, like the frontal, parietal, and occipital bones. Each bone is important for the skull’s structure.
The occipital condyles are key joints that link the skull to the spine. They allow for smooth head movements. The zygomatic arches, or cheekbones, shape the face and hold facial muscles. Knowing about these parts is key because they affect how dogs eat, interact, and connect with people.
A dog’s skull is part of its skeleton, which has about 321 bones. The skull is crucial for sensing the world and protecting the brain.
| Dog Skull Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Occipital Condyles | Connect skull to spine, allowing head movement |
| Zygomatic Arches | Support facial structures and muscle attachment |
| Cribriform Plate | Supports the olfactory bulbs for smell |
| Maxilla | Houses upper teeth, involved in feeding |
In summary, the dog skull anatomy has a complex set of bones. Each bone plays a unique role in the dog’s function and behavior. Looking at these details helps us see the variety among breeds and their special features.
Functionality of the Dog Skull
The design of the dog skull is key for survival. It helps with sensory perception and feeding. Each type of skull has special features that boost certain abilities.
Role in Sensory Perception
The dog skull functionality is vital for sensing the world. The skull’s shape, like the optic chiasm’s position, affects how dogs see. Research shows that the angle of the optic canal varies among breeds.
For example, brachycephalic dogs have an average angle of 93.74 ± 16.00°. This helps them see better. The size and shape of their nasal cavities also boost their sense of smell.
Importance for Feeding
The feeding anatomy of dogs is closely tied to their skull. Brachycephalic breeds have strong jaws for eating. Their shorter skulls, averaging 11.39 ± 1.76 cm, help them bite harder.
On the other hand, dolichocephalic breeds like greyhounds have longer skulls. This suits their eating habits. Dogs have 28 baby teeth and 42 adult teeth, perfect for their meat-eating diet.
Dog Skull Identification
Understanding dog skull identification is key for vets and researchers. It helps them know about health issues and behaviors in different breeds. By analyzing skulls, they can tackle specific traits in various breeds.
Analyzing Different Breeds
Every dog breed has its own skull features. These features tell us about the breed and its behavior. For example, brachycephalic dogs have short snouts, while dolichocephalic breeds have long skulls.
This variety in skull shape has developed over thousands of years. Archaeological finds show dogs have been with humans for over 20,000 years.
Using CT Scans for Identification
CT scans are a modern tool for studying dog skulls. They let us see inside the skull, helping us identify dogs better. By looking at details like the frontal sinuses, vets can tell dogs from coyotes and foxes.
| Feature | Brachycephalic | Mesocephalic | Dolichocephalic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skull Shape | Short and wide | Medium length | Long and narrow |
| Common Breeds | Bulldogs, Pugs | Beagles, Bulldogs | Greyhounds, Collies |
| Health Issues | Respiratory problems | Weight management | Dental issues |
| Skull Length (approx.) | 15-20 cm | 20-25 cm | 25-30 cm |
Dog Skull Variations Across Breeds
The study of dog skull variations shows how different breeds have evolved over time. About 31,000 years ago, dogs and wolves started to look different. This change in shape has led to many variations in dog skulls.
A recent study looked at 533 dog skulls from 120 breeds. It found that four main parts explain almost 76% of the skull’s shape. This shows how dog skulls have changed over the years.
Genetics play a big role in how dog skulls look. For example, a specific gene change is common in short-headed breeds. This change affects their skull shape.
To show these differences, here’s a table from a study on dog skull diversity:
| Measure | Brachycephalic Breeds | Dolichocephalic Breeds |
|---|---|---|
| Head Shape Variation | Short and broad skulls | Long and narrow skulls |
| Common Issues | Chiari-like malformation prevalence estimated at 65% | Less documented health issues |
| Genetic Associations | Influenced by BMP3 gene | Varied QTL associations noted |
| Skull Size | Smaller, compact structures | Larger, elongated structures |
This variety in dog skulls shows how breeding has shaped them. It also affects their health and behavior. Ongoing studies are helping us understand this diversity better.
Understanding Dog Skull Anatomy: The Optic Chiasm
The optic chiasm is key in how dogs see the world. It helps them process visual information. Knowing about the optic chiasm and orbital shape gives us a peek into a dog’s vision.
This includes how well they see movement and depth. It’s fascinating to learn about their visual abilities.
Influence of Orbital Shape
The shape of a dog’s orbit affects their vision. Different skull shapes lead to unique orbital shapes. This can change how dogs see the world.
Studies using advanced imaging have shed light on dog vision. They show how orbital shape impacts a dog’s ability to see. This is important for activities like hunting and playing.
Significance of Dog Skull Replicas
Dog skull replicas are very important for learning and in veterinary care. They show the detailed anatomy of dogs, helping us understand different breeds. These replicas are great for students and professionals alike, offering a hands-on way to learn without harming real animals.
Uses in Education
In schools, dog skull replicas are great teaching tools. They help students see the detailed differences in dog skulls, like the shapes of different breeds. There are three main skull shapes:
- Dolichocephalic (elongated), seen in sighthounds
- Mesocephalic (intermediate)
- Brachycephalic (very short and broad), like mastiff-type skulls
These replicas make learning easier, helping future vets and animal science students understand dog bodies better.
Benefits in Veterinary Medicine
In vet medicine, dog skull replicas are also very useful. They help vets learn about breed-specific health issues, making diagnosis and treatment better. By studying these replicas, vets can improve their skills without harming animals.
| Model | Type | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Dog Skull with Didactic Painting | Detailed Model | $1,592.00 |
| Dog Skull with Didactic Painting (Discounted) | Detailed Model | $314.00 (was $385.00) |
| SOMSO Artificial Beauchene Skull of an Adult | Realistic Replica | $253.00 (was $274.00) |
| Numbered Skull Model with Brain & Cervical Vertebrae | Educational Model | $137.99 |
| Premier Skull, 4 part (SK80) | Specialized Model | $898.00 |
| SOMSO Unmounted Artificial Beauchene Skull of an Adult | Realistic Replica | $1,137.00 |
Art and Culture: Dog Skull Art
Canine cultural representations have become popular in modern art. They blend natural anatomy with creative expression. Dog skull art lets artists explore themes like mortality, beauty, and the bond between humans and dogs. You can find intricate designs of dog skulls in paintings and sculptures.
Recently, more people are interested in dog skull aesthetics. About 55 people searched for “skull dog aesthetic” recently. Over 50 Halloween art pieces show its appeal. Categories like “Grunge Dog Aesthetic” and “Feral Dog Aesthetic” show growing interest in different dog aesthetics.
Notable cultural references highlight dog skull art’s place in both popular culture and fine art. Works inspired by “The Witcher” series and “Ancient Magus Bride” show its appeal. These references show how animal skulls fascinate artists across industries.
“Dog skulls represent a significant cultural motif, uniting artistic expression with the deep-seated reverence we hold for our canine companions.”
As interest in skull aesthetics grows, social media buzzes with canine skull art. This digital engagement opens new ways for artists and fans. It pushes the limits of traditional art.
Emerging trends show a growing interest in darker themes like “Dark Aesthetic” and “Creepy Art.” These trends indicate a rise in the market for macabre art. They appeal to collectors and fans who enjoy unique art.
To further illustrate the relevance of dog skull art in cultural contexts, the following table summarizes significant trends and data:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Search Interest | 23,000 searches for dog skull-related content recently |
| Album Sketches | Total of 210 sketches created between 1814 and 1830 |
| Artistic Dimensions | Drawing of dog’s skull: 167 mm x 184 mm |
| Influential Artists | Works by John Frederick Lewis with family ties in arts |
| Symbolic Breeds | Frequent mentions of Doberman, Chow Chow, German Shepherd in tattoos |
Interest in targeting niche markets for dog skull art continues to grow. Aesthetics like “Scary Dogs” and “Wolf Art” drive this interest. As artists and fans dive deeper into canine cultural representations, dog skull art remains captivating. It merges anatomy and creativity.
Real Dog Skulls vs. Replicas
When studying canine anatomy, you face a choice: real dog skulls or replicas. Each has its own educational and ethical sides. Knowing the good and bad of both helps you decide for study, display, or keeping.
Pros and Cons of Real Dog Skulls
Real dog skulls show true anatomy, making learning better. They let you see real bone structure and how bones connect. But, getting them raises questions about ethics, like where they come from and how they affect animals.
Dog skull replicas are a kinder, greener choice. They’re made to look just like real ones but don’t hurt animals. Here’s a side-by-side look at real dog skulls and replicas, showing their ups and downs:
| Aspect | Real Dog Skulls | Dog Skull Replicas |
|---|---|---|
| Authenticity | True anatomical detail | Highly accurate reproductions |
| Ethics | Potential ethical concerns | Humane and sustainable |
| Cost | Varies significantly | Generally more affordable |
| Longevity | May degrade over time | Durable material options |
| Regulatory Issues | Restricted in some areas | No such restrictions |
Both real dog skulls and replicas have their places in education. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks. Your choice depends on what you need, where you are, and what you believe is right.
Where to Find Dog Skulls for Sale
Finding a reliable source for a dog skull for sale is easy. You can look online or in physical stores. Many websites and stores sell real and fake skulls. Each has its own benefits for fans and researchers.
When purchasing skulls, know the difference between real and fake ones. Real skulls come from specialized suppliers. Fake ones are found in educational stores. Here are some places to check:
- Online Marketplaces: eBay and Etsy have dog skull listings. Always check the seller’s ratings and reviews.
- Specialty Educational Suppliers: Carolina Biological Supply sells replicas for learning. They focus on quality and ethics.
- Local Antique Shops: Some shops have unique items, like dog skulls. You can see them in person before buying.
It’s important to think about the law and ethics when buying. Make sure any real skull is bought legally. This helps protect animals and the environment.
Best Products for Dog Skull Anatomy Studies
Studying dog skull anatomy needs good tools and resources. Many products help, whether for students or professionals. This section looks at educational models and compares them, focusing on what makes them special and their prices.
Recommended Educational Models
Some educational models are very useful for studying dog skull anatomy. They use frozen cadavers for hands-on learning. This makes learning about surgery and dissection better. Having real dog skulls to study helps with understanding anatomy and building confidence in surgery.
- Frozen Cadavers: Help develop skills in a safe way, making live animal procedures safer.
- Real and Replica Canine Models: Give students a chance to learn by doing.
- Anatomical Charts: Tools like Canine and Feline Comparison PDF Charts help with structured learning.
Comparative Analysis of Available Products
Looking closely at different products shows there are many options for learning. Knowing about prices and how to get them helps buyers make good choices.
| Product | Type | Price (Excl. VAT) | Delivery Cost | Delivery Time | Return Policy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexibly Mounted Real Canine Skull | Real Skull | £148.00 | £6.00 (for orders | 3 – 12 months | 14 days for unused products |
| Frozen Cadaver Specimens | Frozen Cadaver | Varies | Free for orders > £40 | Contact for details | 14 days for unused products |
| Canine and Feline Comparison PDF Charts | Educational Material | Varies | Free for orders > £40 | Immediate download | No refunds |
Emergence of Dog Breeds and Their Craniofacial Diversity
The journey of dog breeds is fascinating. It’s shaped by domestication and selective breeding. Today, we see a wide range of skull shapes, thanks to environmental and social changes over thousands of years.
Impact of Domestication on Skull Shape
Domestication changed dogs a lot. It started around 33,000 years ago in Siberia. This early time shows how dogs adapted to their new homes.
Dogs faced tough times, like the last ice age, about 26,000 years ago. This made it hard to keep them as pets. Yet, dogs like Tibetan Mastiffs, Newfoundlands, and Siberian Huskies show how they adapted.
Genetic Mechanisms Behind Skull Variations
Studies on DNA show how dog breeds differ. A study with 70 breeds, wolves, and coyotes found common traits. This shows their shared history.
Dogs were domesticated long before farming started. This mix of survival and breeding led to many skull shapes today.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Fossil Age | 33,000 years |
| Similar Breeds | Tibetan Mastiffs, Newfoundlands, Siberian Huskies |
| Timeframe of Domestication | At least 33,000 years ago, possibly 100,000 years ago |
| Environmental Influences | Last glacial maximum occurred around 26,000 years ago |
| Development of Agriculture | Agriculture started roughly 10,000 years ago |
Conclusion: Insights from Dog Skull Anatomy
Studying dog skull anatomy gives us deep insights into the world of canines. Different breeds have unique skull shapes. These shapes tell us a lot about their behavior and health.
Genetics play a big role in these differences. For example, changes in the BMP3 gene affect skull shape. This impacts how dogs eat and their health risks.
Learning about dog skulls helps us give better care to pets. Knowing about skull anatomy is key for safe dental work and surgeries. This knowledge is important for vets, teachers, and researchers.
Exploring dog skull anatomy is more than just learning. It shows how a dog’s body shape affects its health. This knowledge helps us improve how we care for dogs. It shows we care about their well-being and understand their needs.